What Temperature Is a Hot Air Oven?
Hot air ovens are a fundamental tool in both laboratory and industrial environments, widely used for sterilization, drying, curing, and heat treatment processes. The hot air oven temperature can vary greatly depending on the purpose, typically ranging between 50°C and 300°C (122°F–572°F).
Selecting the correct temperature is not simply a matter of turning a dial; it requires understanding the science of heat transfer, material tolerance, and application-specific requirements. Whether you are sterilizing surgical instruments, drying food products, or heat-treating metals, the hot air oven temperature determines efficiency, quality, and safety.
How Does a Hot Air Oven Work?
Principle of Operation
A hot air oven operates on the principle of dry heat transfer, where heat energy is delivered through convection currents inside an insulated chamber. Electrical heating elements or gas burners heat the air, which is then circulated evenly by an internal fan. This uniform circulation ensures that every part of the load experiences the same hot air oven temperature, reducing the risk of underprocessing or overheating.
Main Components
- Heating Elements – Convert electrical energy into heat.
- Fan System – Ensures even air distribution, preventing temperature gradients.
- Temperature Controller – Maintains accurate set points for consistent results.
- Insulated Chamber – Minimizes heat loss and improves energy efficiency.
- Shelving & Load Supports – Allow optimal airflow around items.
Hot Air Oven Temperature Reference Chart
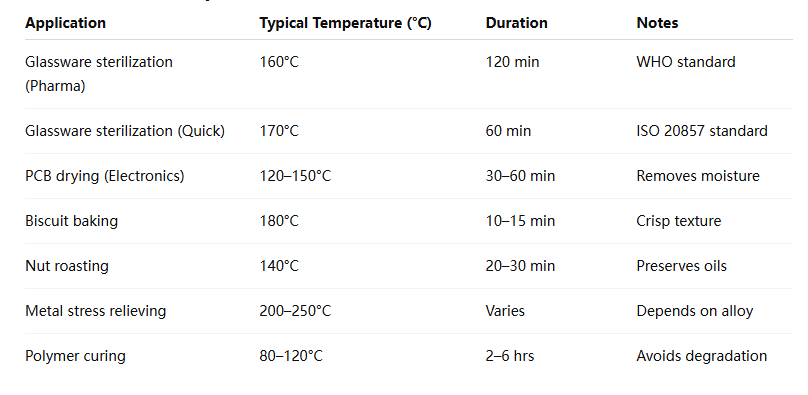
Common Hot Air Oven Temperature Ranges
Low Temperature: 50°C – 100°C
- Gentle drying of moisture-sensitive samples.
- Food dehydration without nutrient damage.
- Preheating delicate materials.
Medium Temperature: 100°C – 200°C
- Standard laboratory sterilization.
- Powder coating curing.
- Removing residual solvents from industrial components.
High Temperature: 200°C – 300°C
- Glassware sterilization in pharmaceutical labs.
- Annealing and stress-relieving metals.
- Electronics component moisture removal before soldering.
Applications of Hot Air Oven Temperature in Industries
Pharmaceutical Industry
Hot air ovens are indispensable for sterilizing metal instruments, glassware, and certain powders.
Standard cycles include:
- 160°C for 2 hours
- 170°C for 1 hour
These hot air oven temperatures are based on killing microbial spores through dry heat. The WHO and ISO 20857 outline exact procedures for validation.
Food Processing
- Biscuits: ~180°C for 10–15 minutes ensures crispness.
- Nuts: ~140°C prevents oil rancidity while preserving flavor.
- Herbs: ~60°C retains essential oils.
Temperature control in food processing ovens is critical — excessive heat can degrade taste, color, and nutritional value.
Metallurgy
Processes like annealing, tempering, and stress relieving depend on exact hot air oven temperature.
Example:
- Annealing low-carbon steel: ~200°C–300°C for several hours.
- Tempering tool steel: ~150°C–250°C to achieve desired hardness.
Electronics Manufacturing
- Drying PCBs at 120°C–150°C before soldering prevents moisture-related defects such as delamination and “popcorning.”
- This is especially important in surface mount technology (SMT) processes.
Research & Materials Testing
Hot air ovens are used for:
- Polymer curing.
- Thermal degradation studies.
- Sample pre-conditioning before tensile tests.
Understanding Temperature Curves in Hot Air Ovens
A well-controlled hot air oven temperature cycle typically includes:
- Preheating Phase – Oven reaches target temperature before loading.
- Ramp-Up Phase – Gradual increase in temperature after loading to prevent thermal shock.
- Holding Phase – Maintaining target temperature for the required duration.
- Cooling Phase – Controlled cooling to prevent sudden temperature drops.
Factors Affecting Hot Air Oven Temperature Selection
- Material Heat Sensitivity – Some degrade above specific temperatures.
- Moisture Content – High moisture requires lower initial heat.
- Load Density – Dense loads may require longer holding times.
- Airflow Design – Poor airflow creates temperature gradients.
Safety Guidelines for Operating a Hot Air Oven
- Preheat to desired hot air oven temperature before loading.
- Avoid blocking airflow inside the chamber.
- Use PPE when handling hot materials.
- Do not exceed manufacturer’s maximum temperature rating.
- Keep combustible materials away from high heat zones.
Calibrating Hot Air Oven Temperature
Calibration steps:
- Place Certified Thermometers inside at multiple points.
- Run Test Cycles to check stability.
- Compare with Display Reading and adjust controller if needed.
Industries like pharmaceuticals require annual calibration to comply with GMP standards.
Energy Efficiency in Hot Air Ovens
- Keep door closed during operation.
- Use high-quality insulation.
- Implement programmable start/stop cycles.
- Regularly clean heating elements and fans for efficiency.
Troubleshooting Temperature Issues

Industry Standards for Hot Air Oven Temperatures
- Pharmaceutical: WHO, ISO 20857.
- Food: HACCP, FDA.
- Metals: ASTM E145 for thermal processing.
Future Trends in Hot Air Oven Technology
- AI-Based Temperature Control – Adapts heating profiles in real time.
- IoT Monitoring – Remote tracking of hot air oven temperature.
- Energy Recovery Systems – Capture and reuse waste heat.
- Smart Sensors – Real-time adjustment to maintain uniformity.
Conclusion
Maintaining the correct hot air oven temperature ensures safety, efficiency, and consistent quality across industries. From pharmaceuticals to electronics, understanding temperature ranges, calibration, and operational protocols is essential.
Chengliankaida Technology Co., LTD, with its expertise in advanced equipment manufacturing, recognizes the importance of precision in temperature control for reliable results.




Comments