In modern minimally invasive surgery, precision, safety, and efficiency are essential to achieving optimal patient outcomes. Among the many specialized tools designed to enhance surgical performance, the Endo Catch bag plays a crucial role. This seemingly simple device allows surgeons to safely retrieve and contain excised tissue or foreign materials during laparoscopic procedures. One of the most important factors when using this device is selecting the appropriate endocatch bag sizes, as it directly impacts surgical efficiency and safety.
This article offers a comprehensive look at the Endo Catch bag’s purpose, its design, applications, and the criteria for choosing the correct size. Whether you are a surgical professional, a student in medical training, or simply curious about how modern surgical devices work, this guide will provide valuable insight.

Understanding the Endo Catch Bag
The Endo Catch bag is a specimen retrieval device designed specifically for minimally invasive surgical procedures, such as laparoscopy. Its primary function is to allow the surgeon to collect, secure, and remove surgical specimens from the body without contaminating the surgical field or damaging the tissue.
Construction and Materials
· Bag Material: Typically made of strong, puncture-resistant polymers to prevent tearing.
· Closure Mechanism: Usually incorporates a drawstring or self-sealing design to secure the specimen.
· Handle and Deployment System: The bag is loaded inside a trocar-compatible applicator that can be easily inserted into the surgical site.
Reusable vs. Single-Use
· While some retrieval bags are designed for multiple uses, most surgical settings prefer single-use Endo Catch bags to minimize the risk of cross-contamination and maintain sterility.
The Primary Use of an Endo Catch Bag
The most important purpose of the Endo Catch bag is safe specimen retrieval. In many surgical cases, especially when removing potentially cancerous tissue or infected material, there is a risk of spreading harmful cells or pathogens within the body cavity if the specimen is not contained properly.
Key Functions
· Preventing Tumor Cell Dissemination – Especially important in oncologic surgeries.
· Avoiding Spillage of Infected Contents – For example, in appendectomy or cholecystectomy procedures.
· Facilitating Controlled Extraction – By containing the specimen, the bag makes removal through a small incision much safer and easier.
Choosing the right endocatch bag sizes for the intended procedure ensures that the specimen fits comfortably without stretching or damaging the bag.
Why Endocatch Bag Sizes Matter in Surgery
Selecting the appropriate endocatch bag sizes is not a trivial decision. Using a bag that is too small may require specimen fragmentation, increasing the risk of contamination. Conversely, a bag that is unnecessarily large may be harder to maneuver in the confined space of the body cavity.
Impacts of Incorrect Size Selection
· Extended Operative Time – Struggling with an ill-fitting bag slows the procedure.
· Potential Bag Damage – Overfilling increases the risk of tears.
· Increased Patient Risk – Spillage or leakage can lead to complications.
For example, in laparoscopic cholecystectomy, a medium-sized bag is often ideal, while in oophorectomy for large cysts, a larger endocatch bag size may be necessary.
Common Endocatch Bag Sizes and Their Applications
Most manufacturers offer multiple endocatch bag sizes to accommodate different surgical needs. While exact dimensions vary by brand, the general categories include:
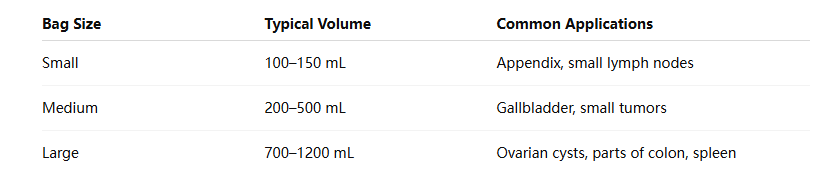
By matching the endocatch bag sizes to the specimen size, surgeons can work more efficiently and reduce the risk of complications.
How to Select the Right Endocatch Bag Sizes
Choosing the right endocatch bag sizes involves several key considerations:
· Assess the Specimen Size – Preoperative imaging can give a good estimate.
· Consider the Surgical Approach – Smaller ports may limit large bag insertion.
· Anticipate Extraction Path – Larger specimens may require slight incision extension.
· Have Multiple Sizes Available – To adapt if intraoperative findings differ from expectations.
Surgeons often plan for at least two potential endocatch bag sizes before the operation to remain flexible.
Surgical Procedures That Commonly Use Endo Catch Bags
While the Endo Catch bag is versatile, certain procedures rely on it more frequently:
· Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy – To retrieve the gallbladder without bile spillage.
· Appendectomy – To contain an inflamed or ruptured appendix.
· Oophorectomy – To safely remove ovarian cysts or tumors.
· Colectomy – For removal of diseased bowel segments.
· Oncologic Laparoscopy – To prevent cancer cell spread.
In each case, endocatch bag sizes must be chosen based on both the expected specimen volume and the working space available.
Best Practices for Using an Endo Catch Bag
Proper handling is critical to avoid bag rupture or specimen loss.
· Deployment: Fully open the bag inside the body cavity before placing the specimen.
· Loading: Gently maneuver the specimen to avoid tearing.
· Closure: Securely close before extraction.
· Extraction: Pull steadily to prevent snagging on tissue or port edges.
Sterility and Safety Considerations
Maintaining a sterile environment is essential. Single-use Endo Catch bags are typically preferred to eliminate the risk of residual contamination. Proper disposal protocols should be followed to ensure safe handling after removal.
Technological Advances in Endo Catch Bag Design
Recent innovations have improved bag performance:
· Leak-Proof Materials – For higher safety in infected cases.
· Self-Opening Mechanisms – Reduce operating time.
· Compatibility with Smaller Ports – Enables use in more minimally invasive surgeries.
Training and Skill in Using Endo Catch Bags
Surgical teams benefit from simulation-based training to improve deployment and extraction skills. This reduces errors, shortens operation times, and ensures correct use of different endocatch bag sizes.
Conclusion: Maximizing Safety and Efficiency
The Endo Catch bag is an indispensable tool in minimally invasive surgery. Correct size selection is essential for efficiency, safety, and patient protection. From small bags for appendectomies to large bags for complex oncologic procedures, understanding endocatch bag sizes helps surgeons plan and execute operations more effectively.
As an example, Kangji Medical, a leading manufacturer of minimally invasive surgical instruments, offers a variety of retrieval bags designed to meet these diverse surgical needs.




Comments